

See more about quick tips for optimisation from Splunk. You can reduce the time searching takes by: We can reduce the lookup time by choosing a smaller time frame on the left or limiting the number of results.
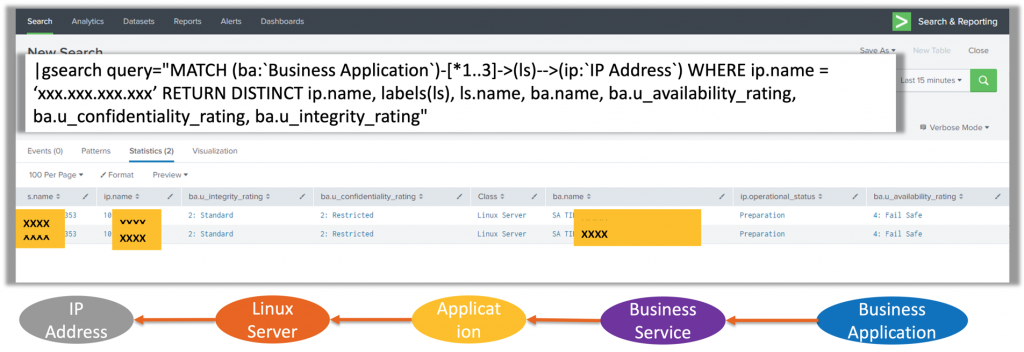
It is good practice to keep our queries concise, otherwise the search could take a long time to run. This retrieves every event because data in Splunk is stored in the indexes. In the figure above I used the query index=* which will match the index field to a wildcard and set the time window to ‘all time’. Queries are made using Splunk’s Search Processing Language (SPL). If a data platform is designed to index any kind of data, then my logs should be in there somewhere.

I have set up Splunk locally with some sample data from the official search tutorial.Ī benefit of using a Splunk deployment is that I don’t have to worry about finding where my data is stored once an application is set up to forward data to the indexers.
#Splunk transaction examples install#
You can also implement or install custom apps. Splunk comes with the search app by default for querying events. Searching with SplunkĪs a developer, the type of machine data I interact with most will naturally be logs output by systems.

#Splunk transaction examples free#
For this blog post, I have set up a free edition of Splunk Enterprise locally. You could set up Splunk manually with Splunk Enterprise, or use their managed solution Splunk Cloud Platform. I want to focus on what you could do with Splunk over the administrative side. This is a very simple overview of the Splunk architecture. Users can access Splunk via the web browser and roles can be assigned to control access. Data is decoupled from the applications that produce it and it is centralised in a distributed system. Splunk can acquire data that is sourced from programs, or manually uploaded files.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
